In the realm of biological sciences, statistical tools are indispensable for validating experimental data and ensuring accurate results. One such essential tool is the Grubbs test, which is specifically designed to detect outliers in a dataset.
What is the Grubbs Test?
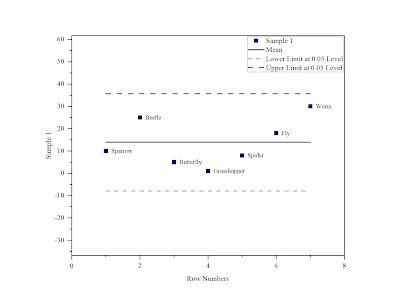
The Grubbs test, also known as the maximum normalized residual test, is a statistical test used to identify outliers in a univariate dataset. Named after Frank E. Grubbs, this test assesses whether the most extreme value in a dataset is significantly different from the rest, indicating it as a potential outlier.
Why is the Grubbs Test Important in Biological Sciences?
In biological research, data integrity is crucial. Outliers can arise due to experimental errors, equipment malfunctions, or natural variability. Identifying and addressing these outliers is vital for maintaining the reliability and validity of the results. The Grubbs test provides a methodical approach to detect such anomalies, helping researchers to make informed decisions about their data.
How is the Grubbs Test Performed?
Performing the Grubbs test involves the following steps:
Calculate the mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ) of the dataset.
Identify the value (Xmax or Xmin) that is furthest from the mean.
Compute the Grubbs statistic (G):
G = |Xi - μ| / σ
where Xi is the value under test.
Compare the computed G value to the critical value from the Grubbs test table.
If G is greater than the critical value, the outlier is considered statistically significant.
Real-World Examples of the Grubbs Test in Biological Research
Gene Expression Studies:
In RNA sequencing, outliers can indicate rare but significant gene expression patterns or errors in measurement. The Grubbs test helps distinguish between the two.
Environmental Biology:
When monitoring pollutant levels in water samples, the Grubbs test can identify erroneous readings due to equipment malfunction, ensuring accurate assessment of environmental health.
Clinical Trials:
In drug efficacy studies, the test can detect anomalous patient responses that might skew the overall results, ensuring more accurate interpretations of the drug’s effects.
Limitations and Considerations
While the Grubbs test is a powerful tool, it has its limitations:
Assumption of Normality:
The test assumes that the dataset follows a normal distribution. If this assumption is violated, the test results may be misleading.
Single Outlier Detection:
It is primarily designed to detect a single outlier. For multiple outliers, other methods like the Generalized Extreme Studentized Deviate (ESD) test might be more appropriate.
Conclusion
The Grubbs test is a valuable tool in the statistical arsenal of biological researchers. By identifying outliers, it ensures the integrity and reliability of experimental data, leading to more robust and trustworthy scientific conclusions. Understanding its application and limitations allows researchers to effectively integrate this test into their data analysis workflow.